CRISES IN THE CAPITALIST SYSTEM:
CRISES IN THE CAPITALIST WORLD
These are the conflicts and problems which upset the capitalist production mainly in Europe and in the colonies especially in Africa and Asia.
These crises were as follows:
1. The First World War
2. The Great Economic Depression
3. The Second World War
1. THE FIRST WORLD WAR
This was the war fought between the members of Triple Entente and the members of Triple Aliance from 28th July 1914 to 11th November in 1918.
· The Triple Alliance was formed by Germany, Italy, Austria-Hungary, Turkey and Bulgaria
· The Triple Entente was formed by Britain, France, Russia, Japan, Romania, Serbia, Belgium, Greece, Portugal, Montenegro and USA
THE TREND OF THE WAR
The WW1 started on 28th July 1914 and ended on 11th November 1914
· The war started first in Balkans Peninsular in which the Austria Hungary heir Archduke Francis Franz Ferdinand and his wife Sophie were assassinated by a Bosnian Serb nationalist Gavrilo Princip on 28th June 1914 in Bosnia capital city Sarajevo.
· The assassination of Ferdinand setoff diplomatic crisis between Austria-Hungary and Serbia because few days later Austria-Hungary government gave Ultimatum to Serbia to submit the assassin but Serbia refused.
· On 28th July 1914 Austria-Hungary invaded Bosnia with support from Russia
· On 2nd August Germany invaded Belgium and Luxemburg and 3rdAugust 1914 Germany declared war against France in the fear that France would help Russia.
· On 4th August the Britain declared war against Germany.
· The USA joined the war on 6th April 1917 to assist the members of the Triple Entente
· The war ended on 11th November 1918 in which Germany was defeated by victorious powers.
THE CAUSES OF THE WW1
The causes for the WW1 can be recognized into two groups namely short term and long term causes.
THE LONG TERM CAUSES
These were the causes which prepared grounds for the occurrence of the war. These factors are as follows.
1. The development of capitalism in the highest stage in 1860’s
This created a stiff competition among capitalist powers such as Germany, France, Britain, Italy and Austria Hungary. For example Germany fought a war with France over the issue of Alsace and Lorain rich region in coal in Franco-Prussian war of 1870-1871. This contributed to the formation of Alliances hence a war.
2. Dissatisfaction in territorial division
The partition of colonies in the Berlin conference of 1884/5 was not fair because some European countries such as Italy was given few colonies compared to other European countries. This created hatred among super powers thus creating grounds for the war.
3. The rise of military alliances
The Germany sought alliance with Austria and signed a Dual Alliance in 1879 with condition that they have to help each other during the war. Italy joined in 1882 to form Triple Alliance. On the other hand France-Russia treaty was signed 1890 to form Entente Cordially and Britain join later to form Triple Entente. The rival alliances created weapons such as bombs, guns, tanks, and created armies which were ready for the war at any time.
4. The France desire to regain Alsace and Lorain
Germany annexed the two provinces in Franco-Prussian war of 1870-1871. This created grounds for revenge among the French men hence preparing ground for WW1.
5. The Balkan crisis
The Balkan nationalism created conflicts between Austria-Hungary and Serbia and between Austria-Hungary and Russia. The competition between the three powers led to the assassination of Francis Ferdinand hence a WW1.
6. Moroccan Crisis 1905 and 1911
The conflict was between France and Germany in which Germany declared independence to Morocco which was a France colony.
THE SHORT TERM CAUSE
The immediate cause for WW1 was the assassination of Archduke Francis Franz Ferdinand on 28th June 1914.
THE IMPACTS OF THE FIRST WORLD WAR ON AFRICA
1. All German colonies such as Tanganyika , Burundi, Rwanda, Namibia, Togo and Cameroon were under League of Nations as mandatory territories. This led to the changing of colonial administrative systems which affected Africans.
2. Deaths among Africans especially in Germany colonies such as Tanganyika and Togo in which the war was fought.
3. The spread of disease such as flue which consumed the lives of thousands of Africans for Example in Tanganyika it is approximated about 7000 people died because of flue.
4. Destruction of properties such as farms, mines and infrastructures like railway were badly destroyed in German colonies.
5. The fall of the external trade between Europe and Tanganyika due to the destruction of European economies such as banks and industries.
6. There was increasing exploitation in the colonies such as land alienation, low wages and introduction of agricultural schemes.
THE IMPACTS OF THE WORLD WAR IN EUROPE
1. The Germany was prevented from building naval ships, airplanes and tanks. The number of her soldiers was limited to 100,000 soldiers.
2. The Germany was required to pay war reparation of 6500 USD million to the winners of the wars.
3. The destruction of economies such as industries and trade. During the war time many industries were closed.
4. Loss of lives for example it is estimated that about 13 million people died while others became disabled and orphans.
5. It led to the formation of League of Nations which guaranteed world peace and security.
6. The Alsace and Lorraine province were returned to France from Germany domination.
7. It led to the Great Economic Depression in 1929-1933 which affected the world economy.
8. The rise of aggressive policies which prompted to occurrence of WW2.
The capitalist production has four major stages.
2. THE GREAT ECONOMIC DEPRESSION 1929- 1933
This was an economic slump crashed capitalist from 29th October 1929 up to 1933. The depression started in USA and spread to Britain, Canada, Italy, France and Austria and in colonies such as Africa and Asia. The black Tuesday 29th October 1929 was the fourth day of the market crash; it was the worst day in the history of New York Stock Exchange and USA in which the stock of 50 companies dropped from $252 to $62 within four days. Two months later stock holders had lost more than 40 billion.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GREAT ECONOMIC DEPRESSION
1. Fall of production in industries due to over production
2. Low prices of crops and goods such as in US the price of wheat declined.
3. Closure of banks in capitalist world for example in US 5000 banks were closed by 1932.
4. Unemployment in the world for example over 30 million people had no jobs in US by 1932.
5. Collapse of the national income.
6. Low wages, foods shortage and poor social services.
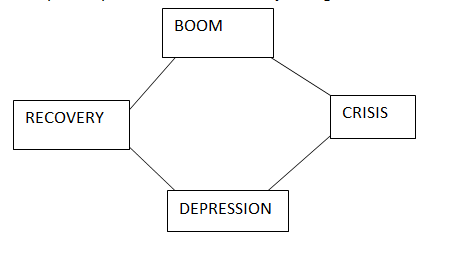
CAPITALIST PRODUCTION CYCLE:
The capitalist production has four major stages.
BOOM STAGE (PEAK)
This is the period when the economy is at the highest level. During this period the economy has the following characteristics:
1. High level of investment
2. Lowest level of employment
3. High standard of living
4. Social and political stability
.
CRISIS
This is the temporary decline in the economic activities and it has the following challenges
1. Decrease in investment
2. Decrease in employment
3. Decrease in income
4. Decrease in trade
5. Decrease of commodity price
DEPRESSION STAGE
This is the period of total decline in the economy or stagnation of the economy. It has the following characteristics;
1. Lowest level of investment.
2. Highest level of employment.
3. Lower standard of living
4. Total closure of enterprises and investment
5. Lowest level of income.
RECOVERY STAGE
This is the period when the economy starts to improve and expand follows after a depression or a recession; It has the following characteristics;
Investments start to expand.
1. Income increase
2. Prices start to rise.
3. Standard of living starts to rise.
4. Opening of Banks.
THE CAUSES OF THE GREAT ECONOMIC DEPRESSION
1. The effects of WW1
The war ruined the economies of almost all European countries. Due to the collapse of economies efforts were made to recover economies by producing as much as possible. This created over production of goods due to low consumption hence Great Economic Depression.
2. High Protective tariffs by US on the imported goods from Europe.
This appealed European countries to put tariffs on US goods as a result market was narrowed to both continents hence over-production and great economic depression.
3. Un-equal distribution of income
The difference in income between capitalist and workers in which workers were paid inversely proportional to what they produced created a gap between production and consumption hence depression.
4. The fall of stock exchange.
Stock exchange is a business term which refers to market in which workers were paid inversely proportional to what they produced created a gap between production and consumption hence depression.
5. The failure of spectators to pay back loans borrowed from banks
Speculators are people who trade commodities, bonds, equities and currencies, the failure to repay the loan affected economy hence great depression.
6. Nature of the capitalist economy
Economists believe that depression was inevitable due to the fact that any capitalist economy has to pass four phases which are cyclic. Boom, Crisis, Depression and Recovery. There for its nature is what driven it to depression.
EFFECTS OF THE GREAT ECONOMIC DEPRESSION AFRICA
1. Drastic fall of the prices of raw materials in the African countries for example the price of sisal exported to Europe dropped from 32 pounds per ton to 12 pounds per ton between 1931-1932.
2. Fall of worker wages; Colonial government reduced the salaries of workers for example in Kenya the worker’s wages fell from 36/=Ksh to 10/= Ksh in 1930.
3. Unemployment; The depression caused unemployment in many African countries because colonial government retrenched some workers and reduced the size of army.
4. The introduction of agricultural schemes such as ground nuts schemes in Gambia and Tanganyika.
5. Intensification of exploitation; post-depression period witnessed the increase of tax, reduction worker’s wages, forced labor, low price of cash crops and long working hours which were introduced by colonialist so as to compensate their economies.
6. Social welfare for example famine and shortage of food because there was little exportation of goods from Europe to Africa.
THE GENERAL EFFECTS OF GREAT ECONOMIC DEPRESSION
1. The great economic depression affected the entire capitalist nations and other small states either directly or indirectly.
2. It led to the bankruptcy of capitalists due to failure of business and closure of enterprises.
3. Social miseries for example famine and shortage of food.
4. The great depression, led to the collapse of the League of Nations.
5. It led to the exploitation of most African resources.
6. The great depression led to the rise of dictatorship states i.e. Nazism in German, Japan and Italy.
7. The great economic depression led to withdrawal of US loans to the European countries.
Figure 1: Family during great depression ,Carlifonia , 1932
Figure 2: Buried machinery in a barn lot; May 1933 on the Great Plains coincided with the Great Depression
MEASURES TAKEN BY THE COLONIAL POWERS TO ALLEVIATE THE IMPACT OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION IN THE COLONIES
Several measures were taken by the colonial powers to revamp the impact of the great depression on the metropolitan economies. This includes the following;
1. The expansion and consolidation of peasant’s cooperation.
2. Intensification of labor recruitment particularly migrant labor was intensified to meet extra labor free demand.
3. Increase of taxation. Taxes of various kinds were introduced after the depression in order to expand source of income for the colonial state.
4. The colonial state allowed peasant to grow prohibited crops in settler’s colonies. For example in Kenya peasant were allowed to grow coffee.
5. African education curriculum was reviewed to give more emphasis to agricultural education.